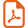
Une partie de est appelée une classe de Vapnik-Cervonenkis si la croissance de la fonction est polynomiale; ces classes se trouvent être utiles en Statistique et en Calcul des Probabilités (voir par exemple Vapnik, Cervonenkis [V.N. Vapnik, A.YA. Cervonenkis, Theor. Prob. Appl., 16 (1971), 264-280], Dudley [R.M. Dudley, Ann. of Prob., 6 (1978), 899-929]).
Le présent travail est un essai de synthèse sur les classes de Vapnik-Cervonenkis. Mais il contient aussi beaucoup de résultats nouveaux, et notamment les deux résultats suivants :
- une partie de est une classe de Vapnik-Cervonenkis si et seulement si le nombre d’atomes de la tribu engendrée par membres quelconques de est majoré par un polynôme en ;
- si est une partie de , chaque loi de probabilité sur la tribu engendrée par définit un écart sur la famille , et on note dim la dimension d’entropie de l’espace ; la famille est une classe de Vapnik-Cervonenkis si et seulement si la quantité Sup est finie.
On trouvera dans l’introduction les énoncés de plusieurs autres résultats nouveaux démontrés ici (dont certains sont indiqués sans démonstration dans ma note [P. Assouad, C.R.A.S., Paris, 292 (1981), 921-924]).
A class of subsets of a set is called a Vapnik-Cervonenkis class if the growth of the function is polynomial ; these classes have proved to be useful in Statistics and Probability (see for example Vapnik, Cervonenkis [V.N. Vapnik, A.YA. Cervonenkis, Theor. Prob. Appl., 16 (1971), 264-280], Dudley [R.M. Dudley, Ann. of Prob., 6 (1978), 899-929]).
The present paper is a survey on Vapnik-Cervonenkis classes. Moreover we prove here many new results, among them the following:
- a subset of is a Vapnik-Cervonenkis class if and only if the number of atoms of the -algebra generated by any collection of members of if no more than (where and are two positive real numbers);
- if is a subset of , every probability law on the -algebra generated by defines a semimetric on the class , and the entropy dimension of the space will be denoted ; the class is a Vapnik-Cervonenkis class if and only if is finite.
The present paper contains other new results, some of them being stated without proof in my note [P. Assouad, C.R.A.S., Paris, 292 (1981), 921-924]).
@article{AIF_1983__33_3_233_0,
author = {Assouad, Patrick},
title = {Densit\'e et dimension},
journal = {Annales de l'Institut Fourier},
pages = {233--282},
publisher = {Institut Fourier},
address = {Grenoble},
volume = {33},
number = {3},
year = {1983},
doi = {10.5802/aif.938},
zbl = {0504.60006},
mrnumber = {86j:05022},
language = {fr},
url = {https://aif.centre-mersenne.org/articles/10.5802/aif.938/}
}
Assouad, Patrick. Densité et dimension. Annales de l'Institut Fourier, Tome 33 (1983) no. 3, pp. 233-282. doi : 10.5802/aif.938. https://aif.centre-mersenne.org/articles/10.5802/aif.938/
[1] , Planes for which the lines are the shortest path, Illinois J. of Math., 22 (1978), 177-190. | MR | Zbl
[2] , Metrics on Rn which possess a Crofton formula, Notices AMS, 26 (1979), A-278.
[3] , A note on pseudometrics on the plane, Z. Warscheinlich keitstheorie, 37 (1976), 145-155. | MR | Zbl
[4] , Espaces métriques, plongements, facteurs, Thèse, Université de Paris-Sud, (1977). | MR | Zbl
[5] , Pseudodistances, facteurs et dimension métrique, Séminaire d'Analyse Harmonique 1979/1980 (Orsay) Publications Mathématiques d'Orsay n° 81-07, pp. 1-33. | Zbl
[6] , Sur les classes de Vapnik-Cervonenkis, C. R. A. S., Paris, 292 (1981), 921-924. | MR | Zbl
[7] , : On a common generalization of Borsuk's and Radon's theorems, Acta Math. Acad. Scient. Hungar., 34 (1979), 347-350. | MR | Zbl
[8] , , Orientability of matroïds, J. of Comb. Th., B. 24 (1978), 94-123. | MR | Zbl
[9] , , Foundations of geometry (english transl.), North Holland (1960).
[10] , Desarguesian Spaces, Proc. of Symp. in Pure Math., 28 (1976), 131-141. | MR | Zbl
[11] . Arrangements d'hyperplans : un chapitre de géométrie combinatoire, Seminaire Bourbaki (1980), exposé n° 651. | Numdam | Zbl
[12] , , , Helly's theorem and its relatives, Proc. of Symp. in Pure Math., 7 (1963), 101-180. | MR | Zbl
[13] , Finite geometries, Springer, 1968. | MR | Zbl
[14] , Central limit theorems for empirical measures, Ann. of Prob., 6 (1978), 899-929. | MR | Zbl
[15] , Balls in Rk do not cut all subsets of (k + 2) points, Advances Math., 31 (1979), 306-308. | MR | Zbl
[16] , Vapnik-Cervonenkis Donsker classes of functions, preprint (1980).
[17] , , Empirical processes, Vapnik Cervonenkis classes and Poisson processes, Probability and Math. Stat., 1 (1981) to appear. | Zbl
[18] , Radon's theorem revisited, In Contributions to geometry, Proc. of the Geometry Symp. in Siegen 1978, Birkhaüser (1979) 164-185. | MR | Zbl
[19] , , Sur les opérations linéaires dans l'espace des fonctions bornées, Studia Math., 5 (1934), 69-98. | JFM | Zbl
[20] , , Proof of Grünbaum's conjecture on the stretchability of certain arrangements of pseudolines, J. Comb. Th, A 29 (1980), 385-390. | MR | Zbl
[21] , Arrangements and spreads, CBMS Regional Conference Series in Math., n° 10 (1972). | MR | Zbl
[22] , Stochastic integration, Markov property and measure transformation of random fields, Ph. D. Dissertation, Berkeley (1979).
[23] , A general theory of convexity, Doct. Dissert., Univ. of Washington (Seattle, 1974).
[24] , , , On a problem of K. Zarankiewicz, Colloquium Math., 3 (1954), 50-57. | MR | Zbl
[25] , Lower bound for the degree of approximation, Trans. Amer, Math. Soc., 97 (1960), 25-34. | MR | Zbl
[26] , Banach spaces with polynomial norms, Pac. J. Math., 82 (1979), 223-235. | MR | Zbl
[27] , Teilungen der Ebene durch Geraden oder topologische Geraden, Math. Z., 64 (1955), 79-102. | MR | Zbl
[28] , Hausdorff measures, Cambridge University Press (1970). | MR | Zbl
[29] , A characterization of Banach spaces containing l1, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 71 (1974), 2411-2413. | MR | Zbl
[30] , On the density of families of sets, J. Comb. Th., A 13 (1972) 145-147. | MR | Zbl
[31] , Metric spaces and positive definite functions, Transact. Amer. Math. Soc., 44 (1938), 522-536. | JFM | MR | Zbl
[32] , Some negative theorems of approximation theory, Michigan Math. J., 11 (1964), 211-217. | MR | Zbl
[33] , A combinatorial problem ; stability and order for models and theories in infinitary languages, Pacific J. Math., 41 (1972) 247-261. | Zbl
[34] , Generalized Radon partitions in convexity spaces, preprint (1980). | Zbl
[35] , Algebric topology, Mc Graw Hill (1966).
[36] , An introduction to number theory, Markham Publ. Co., 1971.
[37] (Marczewski), Ensembles indépendants et mesures non séparables, C.R.A.S., Paris, 207 (1938), 768-770. | JFM | Zbl
[38] , A generalization of Radon's theorem, J. of the London Math. Soc., 41 (1966), 123-128. | MR | Zbl
[39] , , On the uniform convergence of relative frequencies of events to their probabilities, Theor. Prob. Appl., 16 (1971), 264-280. | Zbl
[40] , Partitions by real algebraic varieties and applications to questions of nonlinear approximation, Bull. AMS, 73 (1967) 192-194. | MR | Zbl
[41] , Lower bounds for approximation by nonlinear manifolds, Trans. AMS, 133 (1968), 167-178. | MR | Zbl
[42] , Matroïd theory, Academic Press (1976). | MR | Zbl
[43] , , Some special Vapnik-Cervonenkis classes, Discrete Math., 33 (1981), 313-318. | MR | Zbl
: On 3N points in a plane, Proc. Cambridge Phil. Soc., 55 (1959), 289-293. | MR | Zbl
: Induced subsets, J. Comb. Th., B 12 (1972), 201-202. | MR | Zbl
: Some old and new problems in the independence theory, Colloquium Math., 42 (1979), 127-189. | MR | Zbl
, : Coordinate density of sets of vectors, Discrete Math., 24 (1978), 177-184. | MR | Zbl
: “Dart calculus” of induced subsets, Discrete Math., 34 (1981), 195-198. | MR | Zbl
Cité par Sources :